Methods For Generating Exchnange Or Distribute Keys
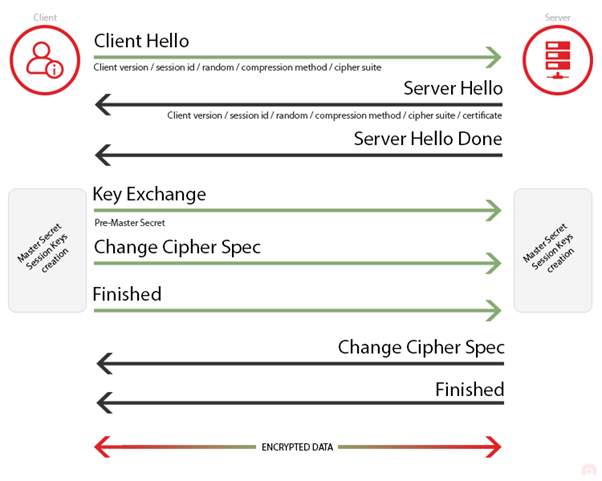
Best way to distribute your key is by using one of the key servers that are available, such as keyserver.ubuntu.com, pgp.mit.edu or keyserver.pgp.com. If you use Seahorse (default key manager under Ubuntu), it automatically syncs your keys to one of these servers. Users can then look up your key using your email address or keyid. Aug 19, 2013 7 Ways to Generate Great Ideas. All of these methods require a commitment of time and energy, but that's the key to great ideas. Outlook Fails To Download OAB. This property is called “Generating server”; in the EMS (Exchange Management Shell) you need to look for the “server” attribute. The OAB on the local disk, in order to enable the Client Access Servers (CAS) to pull it from there for the web-based distribution method. Best way to distribute your key is by using one of the key servers that are available, such as keyserver.ubuntu.com, pgp.mit.edu or keyserver.pgp.com. If you use Seahorse (default key manager under Ubuntu), it automatically syncs your keys to one of these servers. Users can then look up your key using your email address or keyid.
|
Home Energy Generating Methods
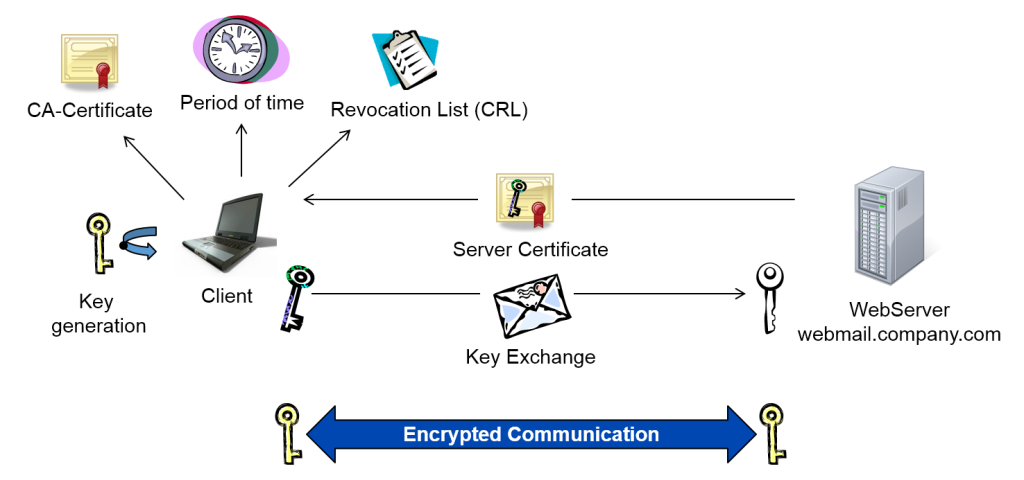
Methods For Generating Exchange Or Distribute Keys Free
- The Diffie-Hellman algorithm is being used to establish a shared secret that can be used for secret. Communications while exchanging data over a public network using the elliptic curve to generate points and get the secret key using the parameters.
- Key generation. The keys for the RSA algorithm are generated in the following way: Choose two distinct prime numbers p and q. For security purposes, the integers p and q should be chosen at random, and should be similar in magnitude but differ in length by a few digits to make factoring.